The Alzheimer & Dementia Today
Alzheimer's & dementia are often confused with each other due to their similar sharing symptoms. But, both of them are named differently for their different nature.
Discover the difference between the two to avoid this mistake and pass it on to your family and friends or any patient or caregiver around you.
WHAT IS ALZHEIMER?
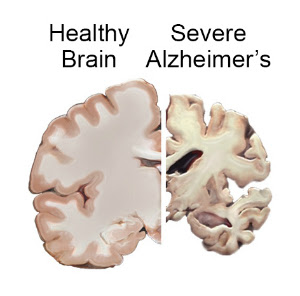
Alzheimer's is an irreversible disease that destroys the brain. It is standouts among the most widely recognized reasons for dementia. Around 50-80 percent of all dementia cases are caused by Alzheimer's. Alzheimer's is a progressive disease which means its symptoms gradually worsen with passing time. It is not a normal part of aging. Yet the greatest known risk factor is increasing age, and the majority of people with Alzheimer's are 65 and older. Alzheimer’s is the seventh leading cause of death in the world.
WHAT IS DEMENTIA?
Dementia is the set of symptoms that occur together, it cannot be called a disease. It damages brain cells. It is linked with declining the memory & thinking process of a person so severely that their ability to perform their routine tasks can be affected.Vascular dementia, which appears after a stroke, is the second most common dementia type. There are numerous different conditions that can cause dementia, including some that are reversible, for example, thyroid issues and vitamin deficiencies.
Dementia is commonly linked to as "senility" or "senile dementia" which reflects the previously popular but incorrect belief that serious mental decline is a normal part of aging. However, according to new research nowadays early onset of dementia is observed at quite a young age.
CAUSES
Alzheimer's is caused by the combination of environmental or genetic factors that affect the brain over time. Some inappropriate lifestyle habits can also lead a person to develop the disease.
Dementia is caused by the loss of nerve cells in the brain as the result of any disease, medicinal side effect, vitamin deficiency or tumor. In some cases, treating the reasons that cause dementia may be beneficial
• drugs
• tumors
• metabolic disorders
• hypoglycemia
SYMPTOMS
These conditions can cause both
• A decline in the ability to think
• Memory deterioration
• communication disorder
• Difficulty remembering recent events or conversations
• Apathy
• Depression
• Impaired judgment
• Disorientation
• Confusion
• Behavioral changes
• Difficulty speaking
• Swallowing
• Walking in advanced stages of the disease
Some types of dementia will share many of these symptoms, but they include or exclude other symptoms that can help make a different diagnosis. for example, Lewy body dementia (LBD) consist of considerable symptoms as Alzheimer’s. Individuals with LBD, however, will probably encounter such as visual hallucinations, difficulties with balance, and sleep disturbances.
HOW ARE THEY DIFFERENT
In Alzheimer's disease, the correct cause can be diagnosed by understanding the symptoms. Also, it is not reversible when the damage has already done in the first place.
Whereas when an individual is diagnosed with dementia, they are diagnosed on the base of their symptoms without actually knowing what's behind the symptoms. Some types of dementia, such as those caused by nutritional problems can be reversed to some extent.
Another real contrast between the two is that Alzheimer's is definitely not a reversible disease. It is degenerative and incurable at this time. Whereas the symptoms of dementia are seen by adverse reactions of medications or vitamin deficiency are really reversible.
DIAGNOSIS
Doctors diagnose Alzheimer's and other types of dementia based on a thorough medical history, a physical examination, laboratory tests, and the specific change in thinking, day-to-day function and behavior linked with each type.
Doctors can decide that a person has dementia with a high level of conviction. Yet it's difficult to define the exact type of dementia in some cases of different dementias because the symptoms and brain changes can overlap.
A doctor may diagnose "dementia" and may not specify a type. If this occurs it may be necessary to consult a specialist such as a neurologist
ALZHEIMER’S TREATMENT
No cure for Alzheimer’s disease is available as of now, but options to help manage symptoms of the disease include.
• Medications for behavioral changes
• Memory-boosting medication
• Alternative treatments that aim to boost brain function and overall well-being
• Medications for improving sleep
• Medications for reducing depression
DEMENTIA TREATMENT
Medications that are used to treat Alzheimer's are the same medications that are sometimes prescribed to help with symptoms of other types of dementia.
Treatment of dementia relies upon its cause. On account of most dynamic dementias, including Alzheimer's disease, there is no cure and no medication that moderates or stops its advancement.
Stay in touch with your doctor if you’re concerned that you have the symptoms of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. Starting treatment promptly can help you manage your symptoms and can help you lead a healthier life. Stay healthy Stay fit.



Comments
Post a Comment